因新兴市场国家外汇储备减少 全球美元头寸短缺危机加剧
因新兴市场国家外汇储备减少,全球美元头寸短缺危机加剧
译者 王为
文中黑字部分为原文,蓝字部分为译文,红字部分为译者注释或补充说明
Global US Dollar Shortage Rises As Emerging Markets LoseReserves
by Daniel Lacalle
The pace at which emerging market economies are losing FX reserves is staggering.In March, emerging economies lost around $1.5 billion in foreign exchange reserves per day,according to Bloomberg.
新兴市场国家的外汇储备总量正在以惊人的速度缩水。据彭博社报道,三月份新兴市场各经济体每天都会流失约15亿美元的外汇储备。
Saudi Arabia alone lost $27 billion in reserves in March, according to Goldman Sachs,and it is one of the countries with the best capacity to endure the current crisis.
据高盛公司统计,三月份仅沙特的外汇储备总量就减少了270亿美元,而沙特还是应对当前经济危机能力最强的国家之一。
China,that still holds $3 trillion in FX reserves despite the crisis, is also among the strongest countries in FX reserves, but the apparently large level is offset by a large US-dollar denominated debt liability. As such, China’s 60% of China’s reserves are there to cover existing liabilities.
尽管危机来临,但中国的手中仍握有3万亿美元的外汇储备,也是在外汇储备方面实力最强的一个国家,但中国的外汇储备中有很大一部分是来自于巨额的美元负债。也就是说,中国有60%的外汇储备将被用于偿还现有的美元债务。
India is also one of the strong countries. As a large importer of commodities, the current slump in activity and lower commodity prices has allowed India to maintain a very healthy level of reserves.
印度也是一个具有很多外汇储备的国家。印度是大宗商品的进口大户,当前经济活动的减少以及大宗商品价格的下跌令印度的外汇储备总量保持在非常充足的水平上。
Which countries are suffering the most? Argentina, Brazil, Mexico, South Africa,Turkey rank among the most impacted.
哪些国家的外汇储备流失最多?阿根廷、巴西、墨西哥、南非和土耳其等国是受影响程度最深的国家。
Whatis causing this collapse in reserves and rising dollar shortage?
是何原因导致外汇储备出现如此大的缩水以及美元短缺状况加剧?
1.The decline in global trade and economic activity due to the forced lockdown weakens export revenues. The outlook for 2020 is bleak with trade possibly declining by between 13% and 32%., according to the World Trade Organization. Some recovery is expected in 2021, but the likelihood of recovering 2019 global trade activity before 2023 is small.
全球贸易和经济活动因强制闭锁措施的实行而减少导致出口收入下降。据世界贸易组织估计,2020年的贸易增长前景不妙,全球贸易总量有可能减少13%-32%。2021年全球贸易活动可能有一些复苏,但在2023年以前恢复到2019年水平的可能性不大。
2.The collapse in commodity prices destroys the trade balance of producer nations. Not only demand is falling to unprecedented levels, but storage is also filling up rapidly and overcapacity at producer nations is building to decade-highs. This problem is not happening just in oiland natural gas, but also in coal, aluminum, soja and, to a lesser extent, incopper.
大宗商品的价格大跌恶化了大宗商品出产国的贸易收支状况。不仅是大宗商品的需求跌到了前所未见的低位,大宗商品出产国的库存也在迅速增加,供过于求的状况到了近十年来最高的水平。这个问题不仅在石油和天然气行业中可以看到,而且也存在于煤炭、铝、大豆加工行业中,在铜加工行业中也存在,虽然程度不大。
3.Local currency collapse leads to central bank intervention. Central banks in emerging economies were smart in 2008-2011 and kept their reserves at very good levels, significantly above foreign currency liabilities. However, the recent slump in many currencies relative to thedollar has caught many emerging market central banks unprepared. Despite themassive increase in the balance sheet of the Federal Reserve and almost unlimited quantitative easing, many emerging currencies have collapsed and ledto their central banks to sell dollars to defend the currency, a big mistake.reserves fall, and the currency remains weak.
本币兑美元的汇率大跌迫使本国央行出手干预。新兴市场国家的央行在2008-2011期间表现得比较聪明,将其外汇储备的总量维持在非常高的水平上,明显高于本国对外债务的总量。但是,最近很多新兴市场国家的货币相对于美元的汇率出现大跌令很多新兴市场国家的央行措手不及。尽管美联储在大幅扩张资产负债表并几乎无限制地实施量化宽松,很多新兴市场国家货币的汇率还是崩溃式下跌并导致本国央行卖出美元以捍卫本国货币的汇率,但这是一个极其错误的做法,外汇储备减少后,其货币对美元的汇率仍跌跌不休。
4.Since 2009, many emerging markets have ignoredthe risk of building imbalances and have entered into large twin deficits, as well as issued record-level of US-dollar denominated debt because domestic and international investors did not want local currency risk. This means that emerging markets face a massive wall of US-dollar denominated maturities of more than $2 trillion in the next two years while refinancing and new debt requirements soar.
2009年以来很多新兴市场国家对本国国际收支账户失衡的风险有所忽视,在贸易收支和财政收支方面双双陷入巨额赤字状态,同时其以美元标价的债务达到创纪录的新高,因本国投资者和国外投资者都不想承担其本币的汇率波动风险。这意味着新兴市场国家在未来两年面临的美元到期债务高达2万亿美元,借新换旧以及增加对外借款的需求大增。
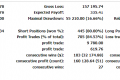
5.The Federal Reserve will continue to increase money supply… But investors have abandoned the risky “carry-trade” of suing cheap dollars to buy high risk emerging market exposure. Understandably,investors have pulled more than $120 billion in emerging market financial assets in March.
美联储将继续增加货币供应量。。。但投资者已放弃了高风险的“利差交易”,即借入低成本的美元资金然后买入新兴市场国家高风险的金融资产。因此很自然地可以看到,三月份投资者将1200亿美元抽离新兴市场国家的金融资产。
The“Sudden Stop” in emerging economies that I warned of in my book Escape from theCentral Bank Trap is happening in front of us. It means that even with massive easing from the Fed, many economies will not see a large flow of funds into local investments, and the countries with the largest fiscal and monetary imbalances simply stop receiving foreign funding.
我在2017年出版的《逃离央行陷阱》这本书里警示过的新兴市场经济体有可能会“突然暂停”的一幕当前正在上演。这意味着即使在美联储实施了巨额的量化宽松之后,很多经济体将不再出现大量外来资金进入本国的一幕,而在财政和货币两方面均存在严重失衡问题的国家将不会再获得外来资金的支持。
Some readers may see this as a great opportunity for China to extend massive loans in Yuan to address the rising shortage of dollars. There is only one problem.The economies that face the sudden stop will sell those Yuan to buy US dollars and repay loan commitments which could create a risk of capital flights in China that the country cannot afford, especially when it is managing its reserve base as well as it can.
一些交易员可能会认为,当前是中国对外大规模推广以人民币计价的贷款以解决美元头寸日益短缺问题的良机。但障碍只有一个,经济活动遭遇突然暂停的国家会卖掉这些来自中国的人民币贷款换取美元然后再还掉贷款有可能给中国带来无法承担的资本外逃风险,尤其是在中国正在竭尽所能管好外汇储备的当下。
The only thing that can reverse the sudden stop or mitigate it is a return tonormal economic activity. Even so, the likelihood of investors jumping on the“negative dollar carry trade” of the past is very low.
唯一能逆转或消除经济活动突然暂停这一局面的是经济活动回归正常。即便如此,投资者像以往一样重拾“负的美元利差交易”的可能性也非常小。
本文地址:https://www.waihuibang.com/currency/usd/146367.html